Gustave
Eiffel’s first work: the Eiffel passerelle, Bordeaux 
a
dream unfulfilled - the transporter bridge [pont transbordeur],
Bordeaux 
a
fifth bridge coming to Bordeaux: pont Chaban-Delmas,
a new vertical lift bridge 
the
6th bridge at Rouen: Pont Gustave Flaubert,
new vertical lift bridge
Ile
de France, Paris: in the context of Abelard and of French
cathedrals 
France’s
western isles: Ile de Ré
France’s
western iles: Ile d’Oleron
Marianne
- a French national symbol, with French definitive stamps
the
calendar of the French Revolution
la
belle époque 
Grand
Palais, Paris
Pic
du Midi - observing stars clearly, A64 
Carcassonne,
A61: world heritage fortified city 
Futuroscope
Vulcania
Space
City, Toulouse
the
French umbrella & Aurillac
50
years old: Citroën DS
the
Citroën 2CV:
a
French motoring icon
mardi gras! carnival
in Basque country
what a hair cut!
m & french pop/rock
country life
in France: the poultry fair
short
biography of Pierre (Peter) Abelard

|
As is usual, the ‘modern’
cathedral was built on the site of previous, less grand,
churches/buildings stretching back to pagan times. As
often, the new building scheme was to replace the burnt
out, previous structure. Of course, they could have refurbished
the old cathedral, as the main cause of cathedral fires
was the wooden forest in the roof and other timbers going
up in flames, leaving the stone core.
Noyon cathedral was as complete as these projects ever
are by about 1235. In 1293, a enormous fire broke out
in Noyon, spreading to the cathedral. By the 18th century,
there were still traces of that fire. Then came the Revolution.
Recovering from that lasted until 1910, and the came the
Germans. They burnt the cathedral out again.

Noyon cathedral, circa. 1900. Source:
Brooklyn Museum

Pillar statue or trumeau, destroyed during the
German bombardments
over
the vaults
A dubious advantage of the destruction of these great
cathedrals during the First World War was being able to look
at the structure of the vaults with the lid off.
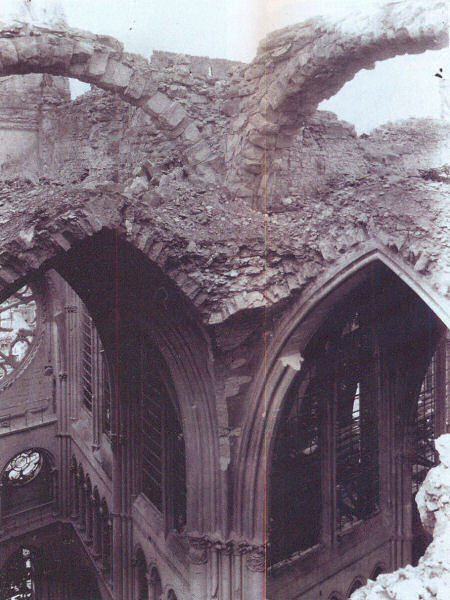

In the above photograph, you can see the
medieval rubble over the vaults of Noyons. You can
see not only the rubble, but also the simple dressed stone
[arches at top] and the more complex, carved stone [columns
and main vaults, lower down].
Noyon cathedral with its roof off during restoration
And here is Noyon cathedral with the roof off and the
rather more tidy concreting, the modern idea of rubble. Of course, this much reduces the fire risk from the traditional and medieval forest.
some
history
The cathedral was the target of much revolutionary zeal
and bile, as Noyon was so closely associated with the
French monarchy. In 1793, the statuary of the west and
transept portals were ordered destroyed, an order that
was carried out with great efficiency. Only four small corbel figures survived, which had
been covered up. So the marvels of the statuary’s
carving has been lost.
Noyon was probably the most important cathedral after
Reims to be widely destroyed during WW1. It was built
very early during the great cathedral building era, being
primarily constructed between 1150 and 1200, though the
cathedral was heavily rebuilt after a major fire in 1293.
Fortunately, its big brother at Laon remained undisturbed. The restoration at Noyon, continuing
almost up to the Second World War, has recovered as much
as could be expected.
The revolutionary government ordered the cathedral be
sold, but the price put on it was so high that this did
not happen, and eventually the horrors of the revolution
receeded. It was used as a hay barn, granary, stable and
dance hall, again the usual combination of dedicated revolutionary
desecration, tempered by utility. |
| |
The
destruction by the Germans during the First World War was much
more extensive.
From With
three armies on and behind the western front, 1918 by Arthur Stanley Riggs (1879-1952).
p.168
“[...] the cathedral [Noyon] is less damaged than I expected:
only the organ shows traces of the invader's sacrilegious hand
- its pipes ravaged to make shell-bands.”
 . .
Noyon cathedral interior, after German WW1
shelling

1918: Noyon cathedral, viewed from the south-east

South side of the nave, 1918
noyon
architecture

The South transept at Noyon, illustrating how the triforium here is below the tribune level.
Image: Columbia
University
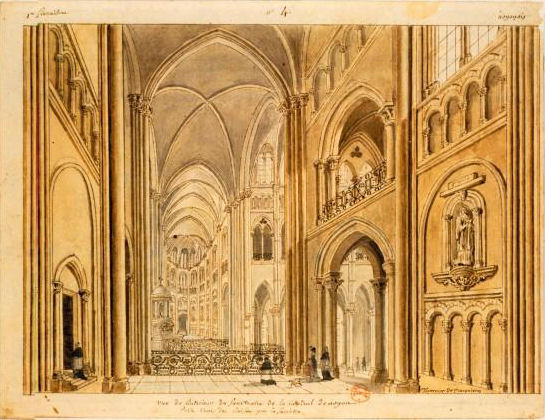

Looking from the north transept across to
the south transept at Noyon cathedral.
Source: Bibliothèque
national de France
Note the unusual features, including
rounded ends, to the transepts, and triforium below the tribunes
in places.
The North transept is unlit on the eastern side,
due to the proximity of the Salle du Trésor [Treasure Room]
built outside at the same time as the cathedral was constructed
(note the blank archway above the doorway on the left).
the
medieval stained glass of noyon cathedral
[The details in this section are unreliable at present.]
With the great travails of history, very little medieval stained
glass survived at Noyon. These two windows probably
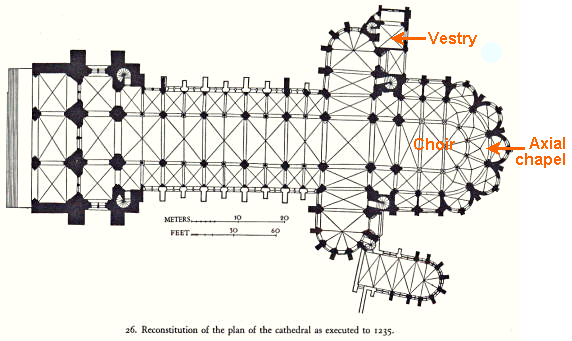
survived because the vestry, where
they had been located, was in a protected corner away
from the main body of the cathedral.
From what I have made out so far, these panels had been
badly damaged and then restored. This is quite common,
even to the extent that fragments of glass were picked
off the ground from amongst the rubble, sometimes after
considerable delay.
Only nine of the twelve panels in the windows are regarded
as reliable. The others probably involve a degree of imagination.
These two windows were moved to the axial
chapel, in the apse behind the choir. They illustrate
the life of Saint Pantaléon.
| Background
facts |
Noyon |
approximate
population : 14 ,240
average altitude/elevation : 43 m
- cathedral dimensions
- total length : 102 m
nave width : 105 m
nave height : 21.5 m
|
bibliography
| Notre-Dame of Noyon
in the Twelfth Century: A Study in the Early Development of Gothic
Architecture by Charles Seymour Jr. |
 |
amazon.com
W W Norton & Co Inc, 1968, pbk
ISBN-10: 0393004643
ISBN-13: 978-0393004649
This is a reprint of a book first
published in 1939 by Yale University Press. |

- Some reference keywords/tags:
- cathedrale,france,germany,1870,1914,1940,invasion,occupation,cathedrale,Noyon,Picardy,Panteleimon,France,
Germany, 1870, 1914, 1918, 1940, invasion, occupation,
cathedrale, church, eglise, cathederal, gothic cathedral
construction, Cathedrale, Gothic architecture, German
bombing, son et lumiere, stained glass windows, Chartres,
Rouen, Poitiers, Dax, Noyon, Reims, Laon, Soissons,
Arras, Cambrai, Saint Quentin, map, diagram, diag, illustration,
photos, image, images, photograph, picture, pics,
end notes
- Corbel
- A projection jutting out to support a weight.
- Big brother in the sense
that it is more unified and has suffered less destruction
and remodelling. Laon, fortunately, survived World War
One and the Revolution reasonably intact. Of course,
Noyon also suffered the great burn-out of 1293.
Comparative sizes of
Noyon and Laon cathedrals |
| |
Noyon |
Laon |
| total length |
102 metres |
110.5 m |
| nave width |
21 m |
30 m |
| vault height |
22.7 m |
24 m |
|